Fibroids, medically referred to as Leiomyoma or myomas, are abnormal growths that develop in the smooth muscle and fibrous connective tissues of the uterus. They are hormone sensitive tumors which typically do not become cancerous, it is said to be the most common benign uterine tumor in women of reproductive age and the commonest reason women undergo surgery.
It is associated with painful period, spotting, excessive bleeding leading to anaemia, lower abdominal pain due to pressure on adjacent organs and disorders of urination and defecation. Fibroids are more common in women of color as compared to the whites. Black women (between 18 -30 yrs.) are diagnosed with fibroids roughly three times as frequently as white women, and tend to develop early, are more numerous and with more symptoms and more likelihood to recur. The reasons for the racial disparity are however poorly understood but certain risk factors have been reported viz.
- Starting periods early.
- Obesity
- Stress
- Lower vitamin D levels.
CAUSES
It’s unclear why fibroids develop but several factors may influence their formation. E.g. Hormones, family history, Pregnancy (increases the production of estrogen and progesterone) e.t.c
TYPES OF FIBROIDS
Fibroids are classified based on their location
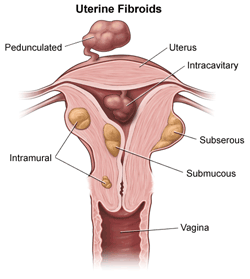 Sub serous – Tend to grow just outside the uterine walls, impacting surrounding organs. As a result, these can put pressure on the bladder, bowels, and abdomen.
Sub serous – Tend to grow just outside the uterine walls, impacting surrounding organs. As a result, these can put pressure on the bladder, bowels, and abdomen.- Intramural – Are the commonest.They are found in the muscles of the Uterus.
- Pedunculated – Hang by a thin thread or stalk inside or outside the uterus.
- Sub-mucous – Protrude underneath the uterine lining and into the uterine cavity, causing issues with uterine function.
- Intra cavitary– Found inside the uterine cavity.
SYMPTOMS
The symptoms of fibroid are a function of size, number and Location and these include:
- Heavy bleeding between or during period.
- Pelvic or lower back Pain.
- Increased menstrual cramping.
- Increased urination.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Menstruation that lasts longer than usual.
- Swelling or enlargement of the abdomen.
The sizes range from ginger nut sized to a watermelon sized. If the fibroids are very small, they may present with no symptoms. The sub mucus fibroids usually cause heavy bleeding, while the very big one can cause obstructive symptoms other symptoms.
DIAGNOSIS
For proper diagnosis, the Gynecologist should do clinical and pelvic examinations and subsequently an imaging technique used.
- ULTRASOUND SCAN (USS)
- Trans abdominal (TAS) – The Ultrasound is done through the abdomen.
- Trans Vaginal-(TVS) – The ultrasound wand is inserted into the vagina to provide clearer pictures since it’s closer to the uterus during this procedure.
- PELVIC MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (PELVIC MRI)
- CT-SCAN
- HYSTEROSALPINGOGRAPH (HSG)
- HYSTEROSCOPY – This is a surgical procedure where a telescope is inserted into the cavity of the uterus. This would allow assessment of the location of the fibroids in relation the uterine cavity. It is also commonly used to surgically remove sub mucosal fibroids that are causing symptoms.
DIFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Adenomyosis – is a condition in which the inner lining of the uterus (the endometrium), where the period comes monthly, is found in the muscle of the uterus. A sort of ectopic nests of endometrial glands in the uterine muscle. Typically looks like fibroid but can be distinguished with ultrasound scan.
FIBROIDS TREATMENT
The treatment of fibroid is a function of symptoms, size, location, and pregnancy wish, desire to preserve the uterus and can be classed as thus:
-
MEDICAL

-
-
Non –Hormonal
- Tranexamic acid: It is a medication that can be taken for the duration of the menstrual period to reduce the amount of bleeding and works by reducing the breakdown of blood clots in the womb.
- Mefenamic acid: It is from a group of medicines called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID). It can be taken for the duration of the menstrual period to reduce the amount of bleeding and pain associated with the periods. It works by reducing the levels of the chemical prostaglandin in the lining of the womb and as a result reduces the amount of blood loss and pain associated with the periods.
-
Hormonal
- The combined oral contraceptive pill: This contains the hormones estrogen and progesterone and often reduces the amount of menstrual blood loss by suppressing ovulation. It can be considered as an option in treating heavy menstrual blood loss in women with fibroids.
- The levonorgestrel releasing intrauterine system: This device releases levonorgestrel (progestogen hormone) into the cavity of the womb and reduces menstrual blood loss by thinning the lining of the womb. It can be considered as an option in treating heavy menstrual blood loss in women with fibroids but would not be suitable for women with large fibroids that are distorting the shape of the uterine cavity.
- Gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GNRH) agonists: These are given in the form of injections and can help shrink fibroid size by switching off ovulation and lowering the levels of the hormone estrogen. They can reduce the heavy menstrual blood loss in women with fibroids but can only be used for a limited period of time (generally up to 6 months) in premenopausal women as it may increase the risk of thinning of the bones (osteoporosis) and therefore its use in clinical practice is limited to use for reduction of fibroid size before surgery.
- Ulipristal acetate: This is a new medical treatment which can help by reducing size of fibroids. It works by blocking the effect of the hormone progesterone, which is thought to play a role in fibroid development. The treatment involves taking one tablet a day. The treatment is initially given daily for 3 months and sometimes prior to surgical removal of the fibroid. If continuing with medical rather than surgical treatment, the 3 month cycle can be repeated for up to 4 cycles. This however, may be associated with liver toxicity and liver function monitoring is required in women taking this medication.
- Medical treatment of fibroids is generally more effective in women with small fibroids and is less likely to be successful in women with multiple or large fibroids.
-
-
SURGICAL
-
-
Surgical ( Invasive)
- Myomectomy / Myomectomy-Hysterectomy
- Interventional Radiology – (Umbilical Artery Embolization (UAE) –A minimally invasive procedure. Here, a real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy is used to guide the delivery of embolic agents to block the arteries that provide blood supply to the fibroids and cause them to shrink.
- Laparoscopic Myomectomy – Used to be the gold standard for women with symptomatic fibroids who wish to be Pregnant
-
Surgical (Non-invasive)
- High-intensity focused Ultrasound (HIFU) or MRgFUS- Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound) – Here, real time ultrasound and high intensity ultrasound waves at a frequency of more than 20,000Hz per second (beyond the normal hearing range for humans) in conjunction with image guidance is used to generate localized heat (>55c) to specifically target individual fibroids, thus destroying their cells. The people with adenomyosis, persons not fit for surgery and also those who wish to avoid surgery can benefit from this procedure. This technology was introduced in 2002 at the University of Oxford, UK and in 2004 in the USA and since then, the technology has been introduced in several countries of the world.
- Advantages
- Non-Invasive.
- Minimal Hospitalization.
- Short recovery time.
- No blood loss, so no need for transfusion.
- Low complications.
- Fertility is preserve.
- Social and economic cost in days lost of work and production are minimized.
-
-
- Preparation before the procedure
-
-
- A preparatory MRI with contrast media must be done before carrying out this procedure. EKG, Chest X-Ray and lab test-Complete blood count, Renal and liver function tests etc. should be done.
- No sex 3 days prior to treatment.
- Intrauterine contraceptive devices should be removed.
- The pubic area should be shaved.
- The bowel should be prepared with enema.
- Diet requirements
- Patient should be on light diet, low in vegetable and beans at least 3 days before the procedure.
- Light diets 24 hrs. Before the procedure. Nil per oral 8 hrs. to the procedure.
-
-
- Post procedure
-
-
- Lie prone 2 hrs. Post procedure.
- Fluid diet can be taken 2hrs after and normal diet a day later.
- No sex after treatment till the next period and temporary contraceptive measures are advised for few months. Intrauterine contraceptives can be inserted 3 months later.
- Follow up Ultrasound or MRI advised 3,6,12 months later following the procedure.
-
CHANGES THAT CAN OCCUR WITH FIBROIDS
All fibroids need oxygenated blood to live, but when they become too large too fast, the tissue can actually outgrow its blood supply. This causes the fibroid to shrink down to a size that the current blood supply can feed.A shrinking fibroid sounds like a good thing,but in reality, it is likely to expand and degenerate again, starting the process over. As a result of this cycle of growth and shrinkage, many women can experience additional symptoms:
- Acute Stabbing pain
- Fever
- Bleeding
- Chronic pain
Other degenerative changes include calcification, cystic degeneration, Hyaline, myxoid and Necrobiosis or red degeneration (as seen in pregnant women) and it is characterized by bleeding and sever abdominal pains.
WHAT EFFECT WOULD MENOPAUSE AND HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT) HAVE ON FIBROIDS?
Fibroids often shrink in size after the menopause as a result of the fall in the levels of estrogen hormone. This reduction is size is likely to be smaller in women receiving HRT as fibroids would be sensitive to the replaced hormones (estrogen and progesterone). However, this effect is unlikely to be significant as the level of hormones supplied through HRT is less than that in natural cycles and having fibroids would not be a contraindication to receiving or continuing with HRT.
In conclusion, if you present with any of the above listed symptoms, please, see your GP or Gynecologist for examination, proper Diagnosis and the best possible management for you.

