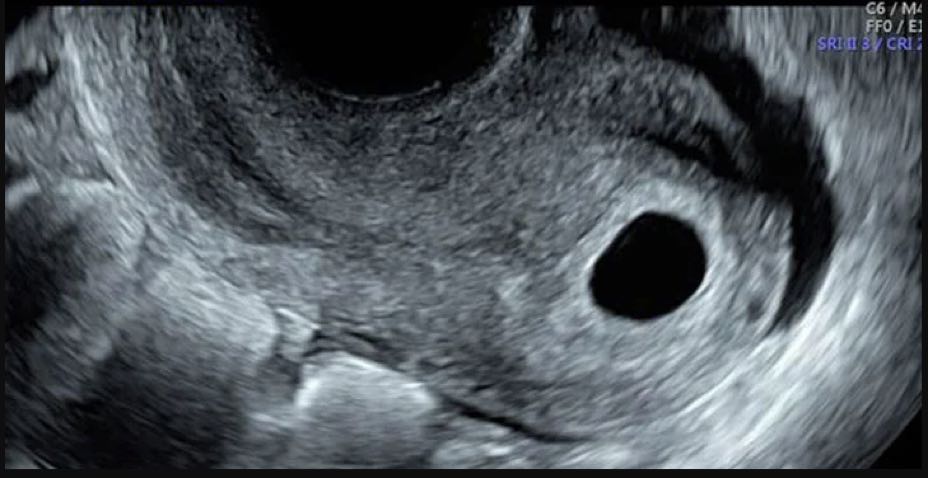
An embryo should be visible by imaging techniques between 6-8 weeks of pregnancy, but with anembryonic pregnancy, the gestational sac is empty.
The sperm and egg unite in one of the fallopian tubes to form a one-celled entity called a zygote soon after fertilization, the zygote travels down the fallopian tube toward the uterus. At the same time, it begins dividing to form a cluster of cells resembling a tiny raspberry, a morula.
The rapidly dividing ball of cells now known as a blastocyst burrows into the uterine lining (endometrium). This process is called implantation.
Within the blastocyst, the inner group of cells will become the embryo while the outer layer will give rise to part of the placenta, which nourishes the baby throughout the pregnancy.
What is Anembryonic Pregnancy?
This is a form of a failed early pregnancy where a gestational sac develops, but the embryo does not form. It is also called a blighted ovum.
When a fertilized egg implants into the uterus but does not develop into an embryo. The embryo will stop growing, but the gestational sac (where the embryo would have developed) continues to grow.
The placenta and empty gestational sac will release pregnancy hormones even without an embryo present. This causes the early symptoms of pregnancy with even a positive pregnancy test.
Presentations
The patient may have no symptoms, alternatively, she may present with the following:
- Anembryonic pregnancy (blighted ovum) may have the same symptoms associated with pregnancy, such as:
-
- A positive pregnancy test.
- Sore breasts.
- A missed period.
- As the pregnancy ends, symptoms may include those of miscarriage, these can include:
-
- Vaginal spotting or bleeding or passage of light grey tissue or blood clots.
- Abdominal cramping.
- The disappearance of breast soreness.
What Are The Causes Of Anembryonic Pregnancy?
This condition isn’t caused by anything that you did or didn’t do, either during or before your pregnancy. The exact cause of anembryonic pregnancy (blighted ovum) isn’t known. It’s thought to be caused by chromosomal abnormalities occurring within the fertilized egg. This may be the result of genetics, poor-quality eggs or sperm
Anembryonic pregnancy has been linked to abnormalities within chromosome 9 (Research shows that several genes that control cell growth and division are located on chromosome 9.
Many of these genes are tumour suppressors, which means they normally help prevent cells from growing and dividing in an uncontrolled way). If one has had a repeat anembryonic pregnancy, chromosomal analysis of the embryos may be considered.
Increased risk higher than the general population is also noted in biologically related couples (consanguineous marriage) and most women who have had anembryonic pregnancy can still carry out other pregnancies successfully and have healthy babies.
Investigations
There are no specific investigations but the following may be considered:
- Semen analysis (determine the sperm quality).
- Follicular stimulating hormone (FSH) or anti-mullerian hormone (AMH) tests, which help determine the quality of the egg.
- Preimplantation genetic screening (PGS), is a genetic analysis of embryos done before implantation into the uterus.
Diagnosis Of Anembryonic Pregnancy
Diagnosis of anembryonic pregnancy is by ultrasound scan especially transvaginal ultrasound scan (TVS) when there is:
- No embryos were seen on transvaginal scanning in a gestational sac with a mean sac diameter of more or equal to 25 mm.
- No embryo on follow-up transvaginal scan is done:
- More than 11 days after an initial scan showed a gestational sac with a yolk sac, but no embryo, or
- More than 14 days after a scan showing gestational sac without yolk sac or embryo.
What Are The Treatment Options?
Several treatment options considered are viz:
- Expectant management.
Here, the patient waits for miscarriage symptoms to occur naturally.
-
- The patient is closely followed without intervention for spontaneous and complete passage of tissue.
- Repeat sonograms and trending pregnancy hormone (HCG levels) are employed to confirm the complete passage of tissue.
- A reasonable determination of a down-trending HCG is sufficient.
- Medical Treatment.
This involves taking medication, such as misoprostol (Cytotec), to bring on a miscarriage.
- Surgical Treatment.
-
- Dilatation and curettage (D & C) surgical procedures can be used to remove the placental tissues from the uterus.
- Manual Vacuum Aspiration (MVA) can also be used.
- Psychological management
Even though there isn’t a baby, there has been a loss of a pregnancy. Miscarriages can be emotionally difficult, especially after getting pregnant after a long wait. Just as with any miscarriage, the body and emotional well-being need time to heal and discussion on preparing for another pregnancy is discussed.
It’s typically recommended that you wait for three full menstrual cycles so that your body will have time to recuperate fully and be ready to support pregnancy.
Complications
Serious complications of treatment are uncommon and they include:
- Heavy bleeding/haemorrhage.
- Uterine perforation (from surgical management).
- Infections include fatal sepsis.
- Complications from a missed ectopic pregnancy.
Conclusion
Having anembryonic pregnancy is emotionally traumatic and even though the main causes are unknown and chromosomal abnormalities have been implicated, most patients that have had anembryonic pregnancy still get pregnant and carry it to term and have normal babies.